13 KiB
Beego
======== Beego is a lightweight, open source, non-blocking and scalable web framework for the Go programming language. It's like tornado in Python. This web framework has already been using for building web server and tools in SNDA's CDN system. It has following main features:
- Supports MVC model, you only need to focus on logic and implementation methods.
- Supports websocket, use customized handlers to integrate sockjs.
- Supports customized router rules, including regex and semanteme.
- Session integration, supports memory, file, redis, mysql, etc.
- Automated parsing user form, you can get data very easy.
- Log level system, easy to record debugging and deployment logs.
- Use configuration file (.ini) to customized your system.
- Use built-in templates in Go, and it provides much more useful functions which are commonly used in web development.
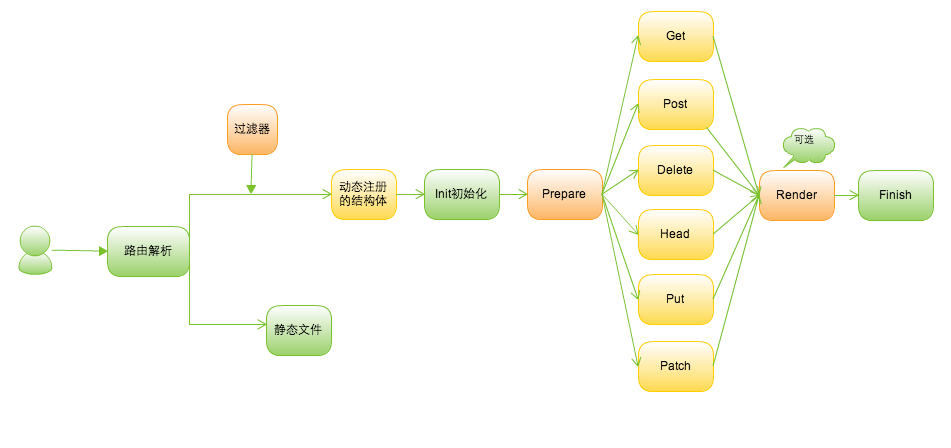
The working principles of Beego as follows.
Beego is licensed under the Apache Licence, Version 2.0 (http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html).
Installation
============ To install:
go get github.com/astaxie/beego
Quick Start
============ Here is the canonical "Hello, world" example app for beego:
package main
import (
"github.com/astaxie/beego"
)
type MainController struct {
beego.Controller
}
func (this *MainController) Get() {
this.Ctx.WriteString("hello world")
}
func main() {
beego.Router("/", &MainController{})
//beego.HttpPort = 8080 // default
beego.Run()
}
http get http://localhost:8080/
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
Date: Sat, 15 Dec 2012 16:03:00 GMT
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
hello world
A more complete example use of beego exists here:beepkg
Some associated tools for beego reside in:bee
Router
============ In beego, a route is a struct paired with a URL-matching pattern. The struct has many method with the same name of http method to serve the http response. Each route is associated with a block.
beego.Router("/", &controllers.MainController{})
beego.Router("/admin", &admin.UserController{})
beego.Router("/admin/index", &admin.ArticleController{})
beego.Router("/admin/addpkg", &admin.AddController{})
You can specify custom regular expressions for routes:
beego.Router("/admin/editpkg/:id([0-9]+)", &admin.EditController{})
beego.Router("/admin/delpkg/:id([0-9]+)", &admin.DelController{})
beego.Router("/:pkg(.*)", &controllers.MainController{})
You can also create routes for static files:
beego.BeeApp.SetStaticPath("/static","/public")
This will serve any files in /static, including files in subdirectories. For example request /static/logo.gif or /static/style/main.css will server with the file in the path /pulic/logo.gif or /public/style/main.css
Filters / Middleware
============ You can apply filters to routes, which is useful for enforcing security, redirects, etc.
You can, for example, filter all request to enforce some type of security:
var FilterUser = func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
if r.URL.User == nil || r.URL.User.Username() != "admin" {
http.Error(w, "", http.StatusUnauthorized)
}
}
beego.Filter(FilterUser)
You can also apply filters only when certain REST URL Parameters exist:
beego.Router("/:id([0-9]+)", &admin.EditController{})
beego.FilterParam("id", func(rw http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
...
})
Additionally, You can apply filters only when certain prefix URL path exist:
beego.FilterPrefixPath("/admin", func(rw http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
… auth
})
Controller / Struct
============
To implement a beego Controller, embed the beego.Controller struct:
type xxxController struct {
beego.Controller
}
beego.Controller satisfieds the beego.ControllerInterface interface, which defines the following methods:
-
Init(ct *Context, cn string)
this function is init the Context, ChildStruct' name and the Controller's variables.
-
Prepare()
this function is Run before the HTTP METHOD's Function,as follow defined. In the ChildStruct you can define this function to auth user or init database et.
-
Get()
When the HTTP' Method is GET, the beego router will run this function.Default is HTTP-403. In the ChildStruct you must define the same functon to logical processing.
-
Post()
When the HTTP' Method is POST, the beego router will run this function.Default is HTTP-403. In the ChildStruct you must define the same functon to logical processing.
-
Delete()
When the HTTP' Method is DELETE, the beego router will run this function.Default is HTTP-403. In the ChildStruct you must define the same functon to logical processing.
-
Put()
When the HTTP' Method is PUT, the beego router will run this function.Default is HTTP-403. In the ChildStruct you must define the same functon to logical processing.
-
Head()
When the HTTP' Method is HEAD, the beego router will run this function.Default is HTTP-403. In the ChildStruct you must define the same functon to logical processing.
-
Patch()
When the HTTP' Method is PATCH, the beego router will run this function.Default is HTTP-403. In the ChildStruct you must define the same functon to logical processing.
-
Options()
When the HTTP' Method is OPTIONS, the beego router will run this function.Default is HTTP-403. In the ChildStruct you must define the same functon to logical processing.
-
Finish()
this function is run after the HTTP METHOD's Function,as previous defined. In the ChildStruct you can define this function to close database et.
-
Render() error
this function is to render the template as user defined. In the strcut you need to call.
So you can define ChildStruct method to accomplish the interface's method, now let us see an example:
type AddController struct {
beego.Controller
}
func (this *AddController) Prepare() {
}
func (this *AddController) Get() {
this.Layout = "admin/layout.html"
this.TplNames = "admin/add.tpl"
}
func (this *AddController) Post() {
//data deal with
this.Ctx.Request.ParseForm()
pkgname := this.Ctx.Request.Form.Get("pkgname")
content := this.Ctx.Request.Form.Get("content")
beego.Info(this.Ctx.Request.Form)
pk := models.GetCruPkg(pkgname)
if pk.Id == 0 {
var pp models.PkgEntity
pp.Pid = 0
pp.Pathname = pkgname
pp.Intro = pkgname
models.InsertPkg(pp)
pk = models.GetCruPkg(pkgname)
}
var at models.Article
at.Pkgid = pk.Id
at.Content = content
models.InsertArticle(at)
this.Ctx.Redirect(302, "/admin/index")
}
View / Template
============
template view path
The default viewPath is /views, you can put the template file in the views. beego will find the template from viewpath.
also you can modify the viewpaths like this:
beego.ViewsPath = "/myviewpath"
template names
beego will find the template from viewpath. the file is set by user like:
this.TplNames = "admin/add.tpl"
then beego will find the file in the path:/views/admin/add.tpl
if you don't set TplNames,beego will find like this:
c.TplNames = c.ChildName + "/" + c.Ctx.Request.Method + "." + c.TplExt
So if the ChildName="AddController",Request Method= "POST",default TplEXT="tpl"
So beego will file the file in the path:/view/AddController/POST.tpl
autoRender
In the controller you needn't to call render function. beego will auto call this function after HTTP Method Call.
You can disable automatic invokation of autorender via the AutoRender Flag:
beego.AutoRender = false
layout
beego supports layouts for views. For example:
this.Layout = "admin/layout.html"
this.TplNames = "admin/add.tpl"
In layout.html you must define the variable like this to show sub template's content:
{{.LayoutContent}}
beego first parses the TplNames files, renders their content, and appends it to data["LayoutContent"].
template function
beego support users to define template function like this:
func hello(in string)(out string){
out = in + "world"
return
}
beego.AddFuncMap("hi",hello)
then in you template you can use it like this:
{{.Content | hi}}
beego has three default defined funtion:
-
beegoTplFuncMap["markdown"] = MarkDown
MarkDown parses a string in MarkDown format and returns HTML. Used by the template parser as "markdown"
-
beegoTplFuncMap["dateformat"] = DateFormat
DateFormat takes a time and a layout string and returns a string with the formatted date. Used by the template parser as "dateformat"
-
beegoTplFuncMap["compare"] = Compare
Compare is a quick and dirty comparison function. It will convert whatever you give it to strings and see if the two values are equal.Whitespace is trimmed. Used by the template parser as "eq"
JSON/XML output
You can use beego.Controller.ServeJson or beego.Controller.ServeXml for serializing to Json and Xml. I found myself constantly writing code to serialize, set content type, content length, etc. Feel free to use these functions to eliminate redundant code in your app.
Helper function for serving Json, sets content type to application/json:
func (this *AddController) Get() {
mystruct := { ... }
this.Data["json"] = &mystruct
this.ServeJson()
}
Helper function for serving Xml, sets content type to application/xml:
func (this *AddController) Get() {
mystruct := { ... }
this.Data["xml"]=&mystruct
this.ServeXml()
}
Beego Variables
============ beego has many default variables, as follow is a list to show:
-
BeeApp *App
global app init by the beego. You needn't to init it, just use it.
-
AppName string
appname is what you project named, default is beego
-
AppPath string
this is the project path
-
StaticDir map[string]string
staticdir store the map which request url to the static file path
default is the request url has prefix
static, then server the path in the app path -
HttpAddr string
http listen address, defult is ""
-
HttpPort int
http listen port, default is 8080
-
RecoverPanic bool
RecoverPanic mean when the program panic whether the process auto recover,default is true
-
AutoRender bool
whether run the Render function, default is true
-
ViewsPath string
the template path, default is /views
-
RunMode string //"dev" or "prod"
the runmode ,default is prod
-
AppConfig *Config
Appconfig is a result that parse file from conf/app.conf, if this file not exist then the variable is nil. if the file exist, then return the Config as follow.
-
PprofOn bool
default is false. turn on pprof, if set to true. you can visit like this:
/debug/pprof /debug/pprof/cmdline /debug/pprof/profile /debug/pprof/symbolthis serves via its HTTP server runtime profiling data in the format expected by the pprof visualization tool. For more information about pprof, see http://golang.org/pkg/net/http/pprof/
Config
============
beego support parse ini file, beego will parse the default file in the path conf/app.conf
throw this conf file you can set many Beego Variables to change default values.
app.conf
appname = beepkg
httpaddr = "127.0.0.1"
httpport = 9090
runmode ="dev"
autorender = false
autorecover = false
viewspath = "myview"
this variables will replace the default beego variable's values
you can also set you own variables such as database setting
mysqluser = "root"
mysqlpass = "rootpass"
mysqlurls = "127.0.0.1"
mysqldb = "beego"
In you app you can get the config like this:
beego.AppConfig.String("mysqluser")
beego.AppConfig.String("mysqlpass")
beego.AppConfig.String("mysqlurls")
beego.AppConfig.String("mysqldb")
Logger
============ beego has a default log named BeeLogger which output to os.Stdout.
you can change it output with the standard log.Logger like this:
fd,err := os.OpenFile("/opt/app/beepkg/beepkg.log", os.O_RDWR|os.O_APPEND, 0644)
if err != nil {
beego.Critical("openfile beepkg.log:", err)
return
}
lg := log.New(fd, "", log.Ldate|log.Ltime)
beego.SetLogger(lg)
Supported log levels
- Trace - For pervasive information on states of all elementary constructs. Use 'Trace' for in-depth debugging to find problem parts of a function, to check values of temporary variables, etc.
- Debug - For detailed system behavior reports and diagnostic messages to help to locate problems during development.
- Info - For general information on the application's work. Use 'Info' level in your code so that you could leave it 'enabled' even in production. So it is a 'production log level'.
- Warn - For indicating small errors, strange situations, failures that are automatically handled in a safe manner.
- Error - For severe failures that affects application's workflow, not fatal, however (without forcing app shutdown).
- Critical - For producing final messages before application’s death. Note: critical messages force immediate flush because in critical situation it is important to avoid log message losses if app crashes.
- Off - A special log level used to turn off logging
beego has follow functions:
- Trace(v ...interface{})
- Debug(v ...interface{})
- Info(v ...interface{})
- Warn(v ...interface{})
- Error(v ...interface{})
- Critical(v ...interface{})
you can set log levels like this :
beego.SetLevel(beego.LevelError)
after set the log levels, in the logs function which below the setlevels willn't output anything
after set levels to beego.LevelError
Trace, Debug, Info, Warn will not output anything. So you can change it when in dev and prod mode.